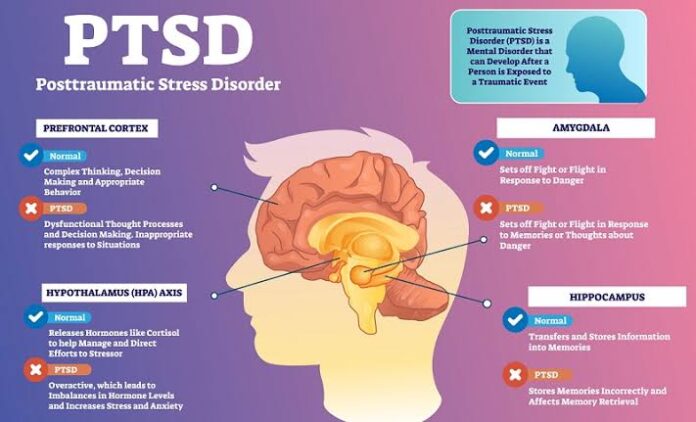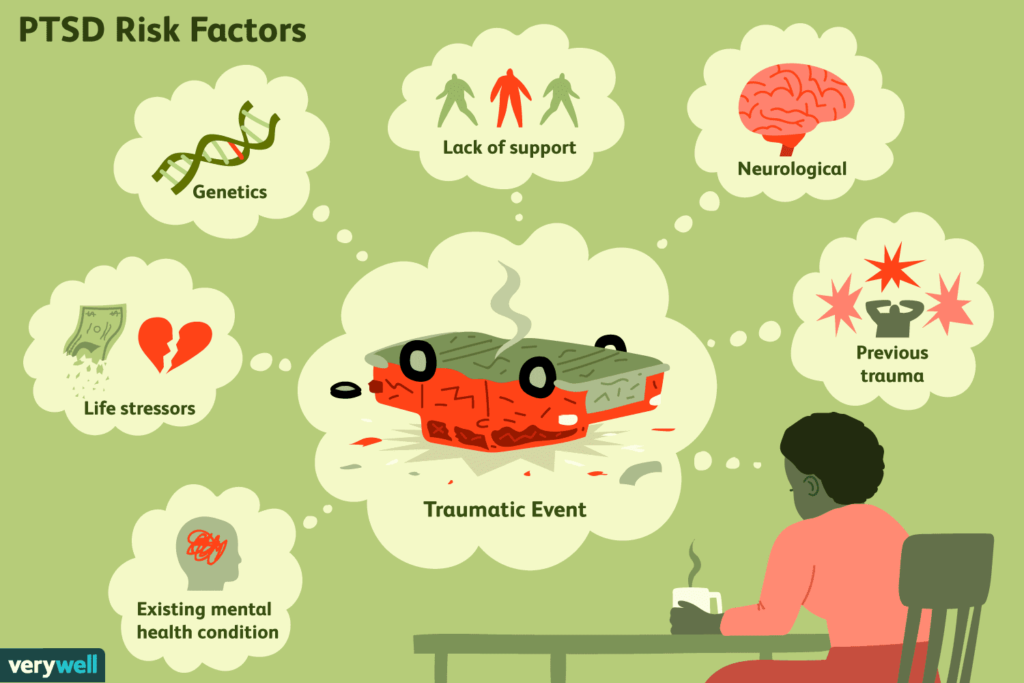
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition triggered by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. This article delves into the symptoms, causes, and various treatment options available for PTSD, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of the disorder and its potential cures.
Symptoms of PTSD
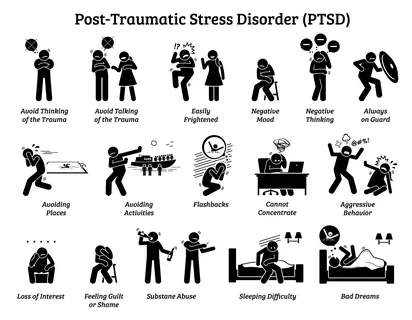
PTSD manifests through a variety of symptoms, which can be categorized into four main types:
- Intrusive Memories:
- Recurrent, unwanted distressing memories of the traumatic event.
- Flashbacks, reliving the traumatic event as if it were happening again.
- Upsetting dreams or nightmares about the traumatic event.
- Severe emotional distress or physical reactions to reminders of the traumatic event.
- Avoidance:
- Trying to avoid thinking or talking about the traumatic event.
- Avoiding places, activities, or people that remind you of the traumatic event.
- Negative Changes in Thinking and Mood:
- Negative thoughts about oneself, other people, or the world.
- Hopelessness about the future.
- Memory problems, including not remembering important aspects of the traumatic event.
- Difficulty maintaining close relationships.
- Feeling detached from family and friends.
- Lack of interest in activities once enjoyed.
- Difficulty experiencing positive emotions.
- Feeling emotionally numb.
- Changes in Physical and Emotional Reactions:
- Being easily startled or frightened.
- Always being on guard for danger.
- Self-destructive behavior, such as drinking too much or driving too fast.
- Trouble sleeping.
- Trouble concentrating.
- Irritability, angry outbursts, or aggressive behavior.
- Overwhelming guilt or shame.
Causes of PTSD
PTSD can develop after an individual has been exposed to a traumatic event. The nature of these events can vary widely but often include:
- Military combat.
- Natural disasters.
- Serious accidents.
- Terrorist attacks.
- Personal assaults, such as rape or robbery.
- Serious health problems, including a life-threatening diagnosis.
The risk of developing PTSD may be influenced by factors such as:
- Intensity and duration of the trauma.
- History of previous trauma.
- Family history of mental health problems.
- Biological factors, such as variations in brain chemistry and function.
A Glimpse into the Future: Promising Treatments
1. Psychotherapy Advances
Recent innovations in psychotherapy have shown promise in not only alleviating PTSD symptoms but potentially leading to long-term recovery:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Enhanced forms of CBT, such as Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) and Prolonged Exposure (PE) therapy, have been refined to better target PTSD symptoms. These therapies help patients reframe negative thoughts and gradually expose them to trauma-related memories in a controlled manner.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR has gained recognition for its effectiveness in reducing PTSD symptoms. This therapy involves guided eye movements while recalling traumatic events, which is believed to help the brain process and integrate these memories more effectively.
2. Pharmacological Innovations
While medications have traditionally been used to manage PTSD symptoms, new drug developments are focusing on targeting the underlying causes:
- MDMA-Assisted Therapy: MDMA (commonly known as ecstasy) has shown remarkable potential in treating PTSD when used in a controlled therapeutic setting. Studies have demonstrated that MDMA can facilitate emotional processing, reduce fear responses, and enhance the therapeutic experience, leading to significant improvements in PTSD symptoms.
- Ketamine: Initially known for its anesthetic properties, ketamine has been found to have rapid-acting antidepressant and anti-anxiety effects. Intravenous ketamine infusions have been explored as a treatment for PTSD, providing relief to patients who do not respond to traditional therapies.
3. Neuroscientific Breakthroughs
Understanding the neurological underpinnings of PTSD has paved the way for innovative treatments:
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): TMS is a non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. Research has shown that TMS can reduce PTSD symptoms by targeting brain regions involved in mood regulation and fear response.
- Neurofeedback: This technique involves training individuals to regulate their brain activity. By providing real-time feedback, neurofeedback helps patients gain control over dysfunctional brain patterns associated with PTSD, potentially leading to symptom reduction.
Treatment Options for PTSD
While PTSD is a challenging condition, effective treatments are available that can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. These treatments include:
- Psychotherapy:
-
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Aims to help individuals change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with PTSD. Two specific types of CBT often used are:
- Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT): Focuses on changing how one thinks about the trauma and its aftermath.
- Prolonged Exposure (PE) Therapy: Involves gradually exposing patients to trauma-related memories and situations to help them confront and process their fears.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): Combines exposure therapy with guided eye movements to help patients process traumatic memories and change their reaction to them.
- Stress Inoculation Training (SIT): A form of CBT that teaches individuals coping skills to manage stress and reduce anxiety.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Aims to help individuals change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with PTSD. Two specific types of CBT often used are:
- Medications:
- Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like sertraline (Zoloft) and paroxetine (Paxil) are often prescribed to help manage PTSD symptoms.
- Anti-anxiety Medications: These can help reduce severe anxiety associated with PTSD but are usually prescribed for short-term use due to the potential for dependency.
- Prazosin: An alpha-blocker that can help reduce or suppress nightmares and improve sleep.
Holistic and Integrative Approaches
In addition to these cutting-edge treatments, holistic approaches play a crucial role in supporting PTSD recovery:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices such as mindfulness meditation and yoga have been found to reduce stress, improve emotional regulation, and enhance overall well-being in PTSD patients.
- Nutrition and Lifestyle: Emerging research suggests that diet, exercise, and sleep play a significant role in mental health. Adopting a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and healthy sleep patterns can support the recovery process.
A Hopeful Horizon
The advancements in PTSD treatment signify a shift from mere symptom management to the possibility of a cure. With ongoing research and the integration of innovative therapies, the future holds promise for those affected by PTSD. By combining traditional approaches with new discoveries in psychotherapy, pharmacology, and neuroscience, we move closer to a world where PTSD can be effectively cured, allowing individuals to reclaim their lives from the shadows of trauma.